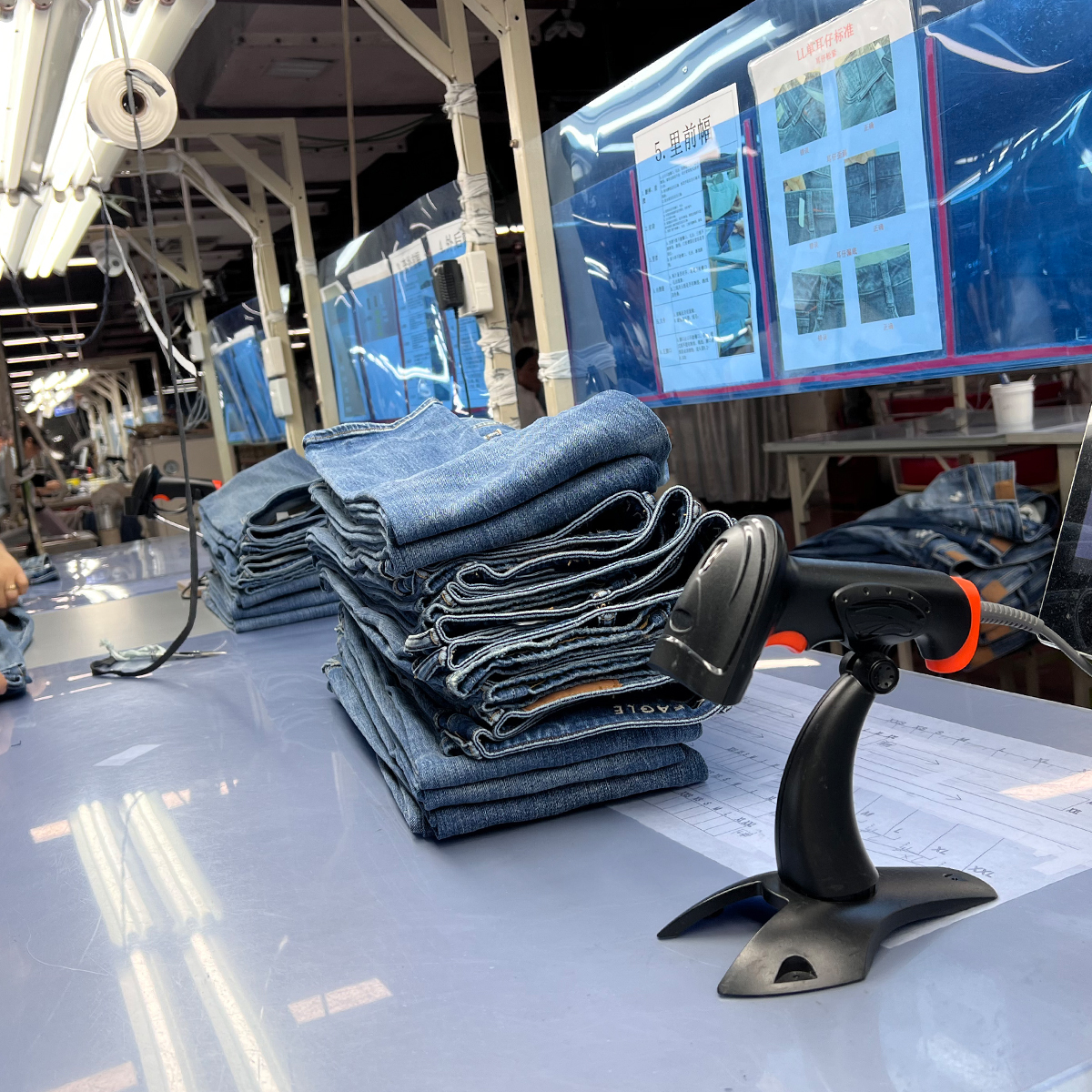
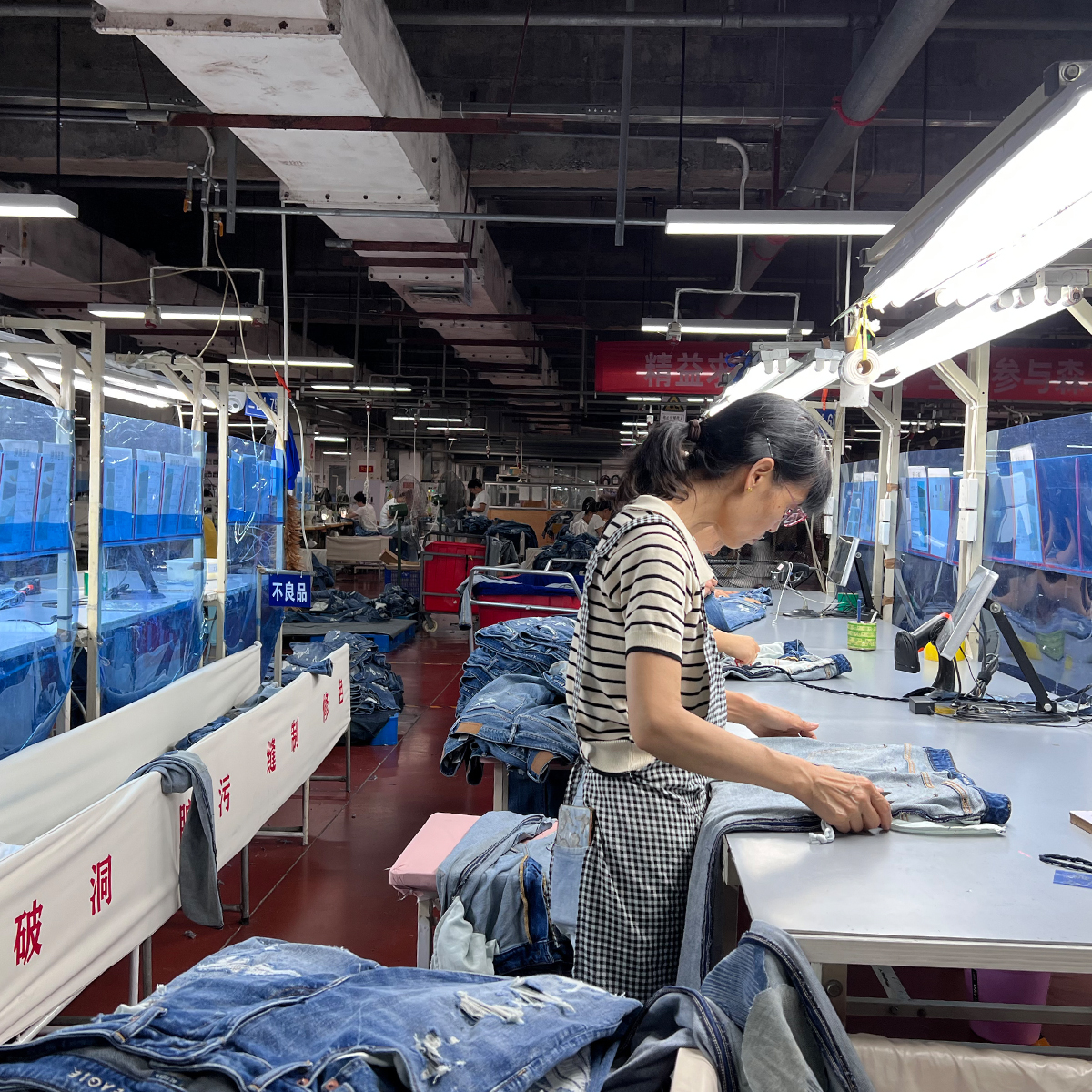
The jeans manufacturing industry in China is a significant player in the global apparel market, known for its vast production capabilities and craftsmanship. However, with this growth comes the critical need for quality control to ensure that products meet international standards and consumer expectations. This article delves into the best practices for quality control adopted by jeans suppliers in China, providing insights for brands looking to maintain product integrity.
Understanding Quality Control in Jeans Manufacturing
Quality control (QC) refers to the processes implemented to ensure that all manufacturing outputs meet specific quality standards. In the context of jeans manufacturing, this entails rigorous testing and inspections at various stages of production. From the selection of raw materials to the final garment, every step is crucial in delivering a superior product that meets market demands.
The Importance of Quality Control
Quality control is not merely a procedural formality; it plays a pivotal role in safeguarding a brand’s reputation. Poorly made jeans can lead to customer dissatisfaction, resultant returns, and a tarnished brand image. In a market as competitive as fashion, maintaining high quality is essential for brand loyalty and long-term success.
Key Stages of Quality Control in Jeans Production
Quality control in jeans manufacturing can be segmented into several key stages, each requiring careful attention to detail:
1. Raw Material Inspection
The first step in quality control is selecting the right raw materials. Denim fabric, threads, zippers, and buttons must all meet specified quality standards. Manufacturers often conduct a thorough inspection of these materials to check for defects such as inconsistencies in fabric dye, weave patterns, or any signs of damage.
2. Pre-Production Planning
Before production begins, companies should create detailed production plans that outline specifications, equipment, and quality standards. This step often involves sampling processes for prototype jeans to test the fit and finish before mass production.
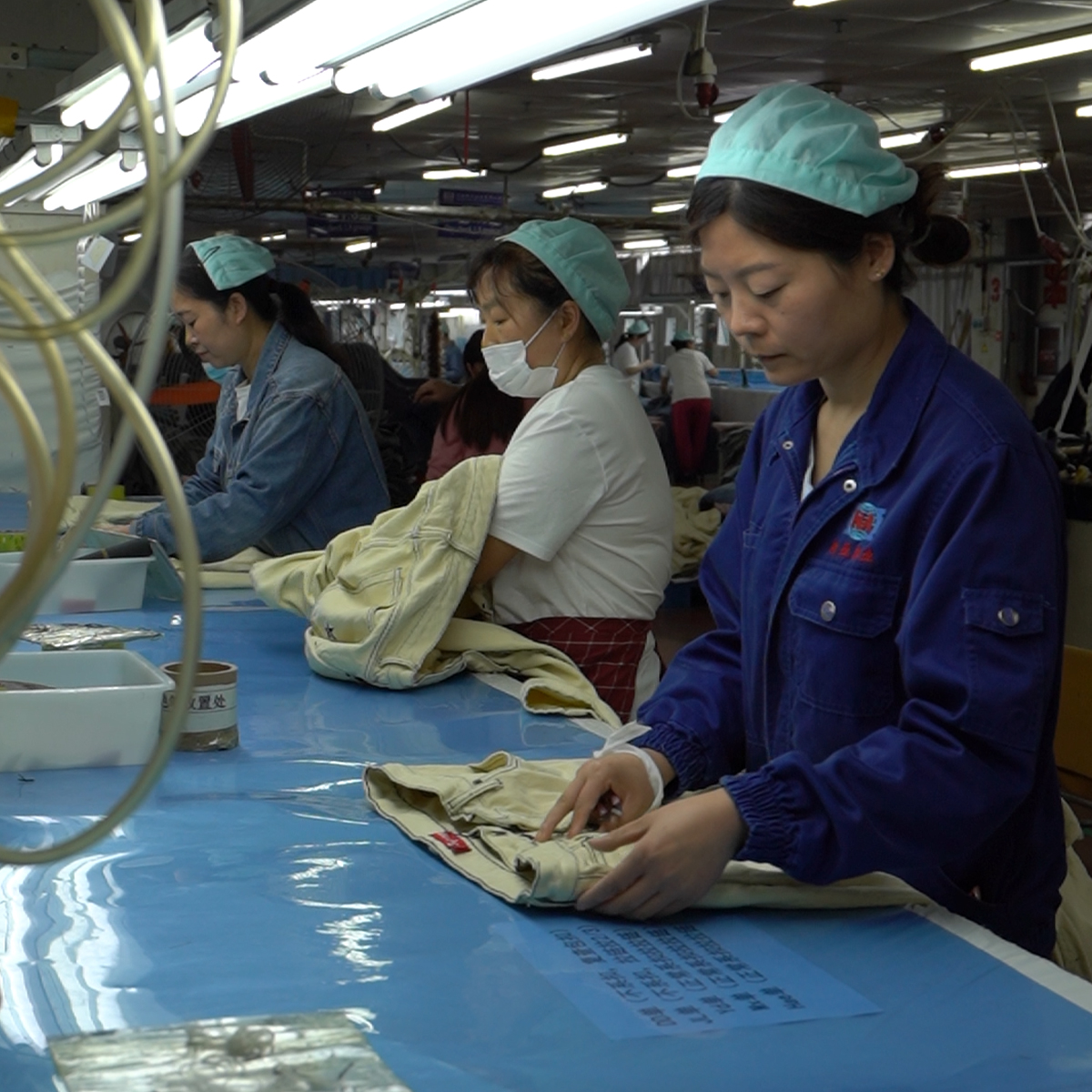
3. In-Process Quality Control
During production, implementing in-process quality control is vital. This includes regular inspections of the production line to ensure that each stage of production adheres to established standards. Techniques like Statistical Process Control (SPC) may be utilized to monitor variances in the production process.
4. Final Inspection
Upon completion of production, a final inspection should take place. This involves a comprehensive review of the finished jeans for any defects and adherence to sizing, stitching, and finishing requirements. Companies may employ third-party inspectors to ensure unbiased evaluations.
Common Quality Control Challenges in Jeans Manufacturing
Despite the utmost efforts in quality control, various challenges may arise. Understanding these common pitfalls can better prepare suppliers and brands to overcome them:
1. Variability in Production
Production variability can originate from differences in raw materials, human error, or machinery malfunction. It is essential to standardize processes and provide thorough training for workers to minimize discrepancies.
2. Supplier Relations
Building effective relationships with suppliers is critical. Discrepancies in material quality delivered by suppliers can significantly impact the final product. Regular communication, audits, and performance assessments can mitigate risks associated with unreliable suppliers.
3. Changing Consumer Preferences
The fashion industry is inherently volatile, with changing consumer trends and preferences. Ensuring that quality control processes remain agile and can adapt to shifting demands is crucial in maintaining relevance in the market.
Innovations in Quality Control
The jeans manufacturing industry is evolving, and so are the methods of quality control. The integration of technology plays a vital role in enhancing QC processes:
1. Automation and AI
The use of automation and artificial intelligence (AI) in production lines has the potential to drastically improve quality control. Automated quality checks can provide real-time data, reducing the likelihood of defects and enhancing overall efficiency.
2. Digital Quality Management Systems
Implementing digital systems for quality management allows manufacturers to maintain comprehensive records of inspections, tests, and audits. Digitalization facilitates better data analysis, enabling companies to identify trends and address issues proactively.
3. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is being explored for its potential in ensuring transparency and traceability in supply chains. By allowing manufacturers and brands to track each step of the production process, blockchain can enhance accountability and quality assurance.
Best Practices for Brands Collaborating with Chinese Jeans Suppliers
For brands looking to collaborate with Chinese jeans manufacturers, certain best practices can help ensure a successful partnership:
1. Conduct Thorough Research
Before selecting a supplier, brands should conduct extensive research. Investigate the supplier’s reputation, product range, certifications, and client feedback. This knowledge is crucial in selecting a reliable partner.
2. Establish Clear Quality Standards
Establishing clear expectations for quality standards from the outset can help eliminate misunderstandings. Utilize detailed documentation to outline specifications, testing requirements, and approval processes.
3. Foster Collaboration
Encouraging an open line of communication between brands and suppliers is essential. Regular meetings, sharing quality reports, and feedback allow both parties to work collaboratively toward achieving quality objectives.
4. Perform Regular Audits
Scheduling regular audits of the manufacturing process and facilities can ensure compliance with quality standards. These audits can help identify areas of improvement and foster a culture of quality within the supplier’s team.
Conclusion
Emphasizing quality control in jeans manufacturing not only benefits the suppliers but also ensures customer satisfaction. With robust practices and a proactive approach to quality assurance, brands can confidently enter the competitive apparel market, gaining trust and loyalty among consumers while enjoying long-term success.