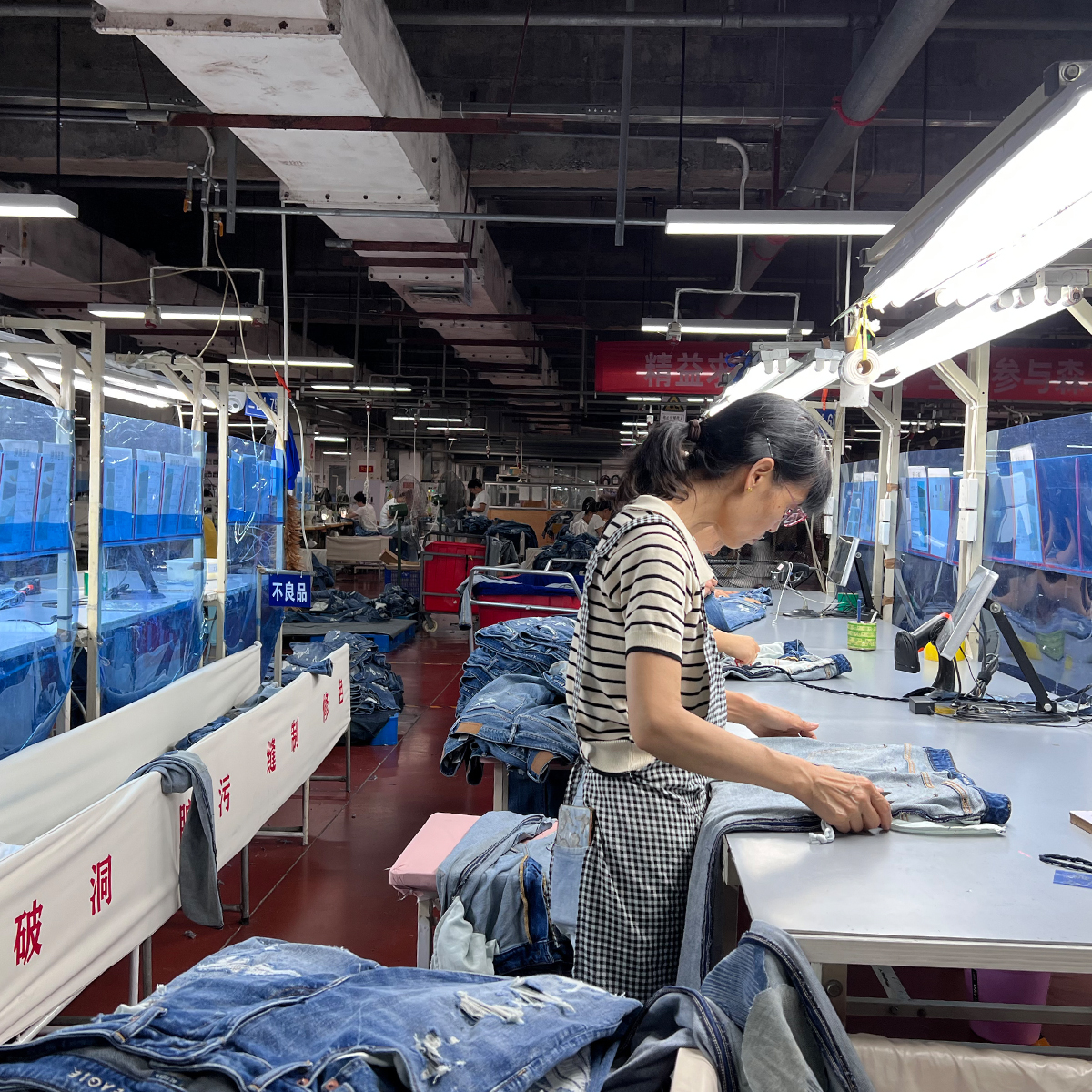
In the fast-paced world of fashion, denim remains one of the most resilient and versatile fabrics. Consumers demand durable, well-fitting jeans that look good across seasons, while brands chase speed to market and sustainable production. The answer to these conflicting pressures lies in the smart transformation of jeans manufacturing. Smart jeans manufacturing combines automation, data-driven decision making, and flexible processes to deliver high-quality jeans faster, with lower waste and better traceability. This article explores what makes jeans “smart,” how a modern denim factory operates, and how brands and contract manufacturers can adopt these innovations to stay competitive in a global market.
What makes jeans “smart”?
The term smart jeans refers to the integration of digital tools, automation, and analytics across the entire value chain—from design and development to cutting, sewing, finishing, and quality control. The goal is to reduce manual variability, increase throughput, and create a transparent trail of information for each garment. Key components of a smart jeans operation include:
- Digital pattern development and grading: Computer-aided design (CAD) and pattern software generate precise, repeatable patterns and can quickly scale sizes for dozens of SKUs.
- Automated fabric cutting and material handling: Computer-controlled cutting machines or laser systems optimize fabric utilization and reduce handling damage.
- Robotics and automated sewing: Modern sewing stations, robotic assists, and seam automation improve consistency and reduce operator fatigue.
- Inline quality control and computer vision: Cameras, sensors, and AI algorithms detect defects in real time, preventing imperfect pieces from progressing down the line.
- Factory-wide data integration: ERP/MES/PLM systems connect design, planning, production, and logistics, enabling real-time visibility and better decision making.
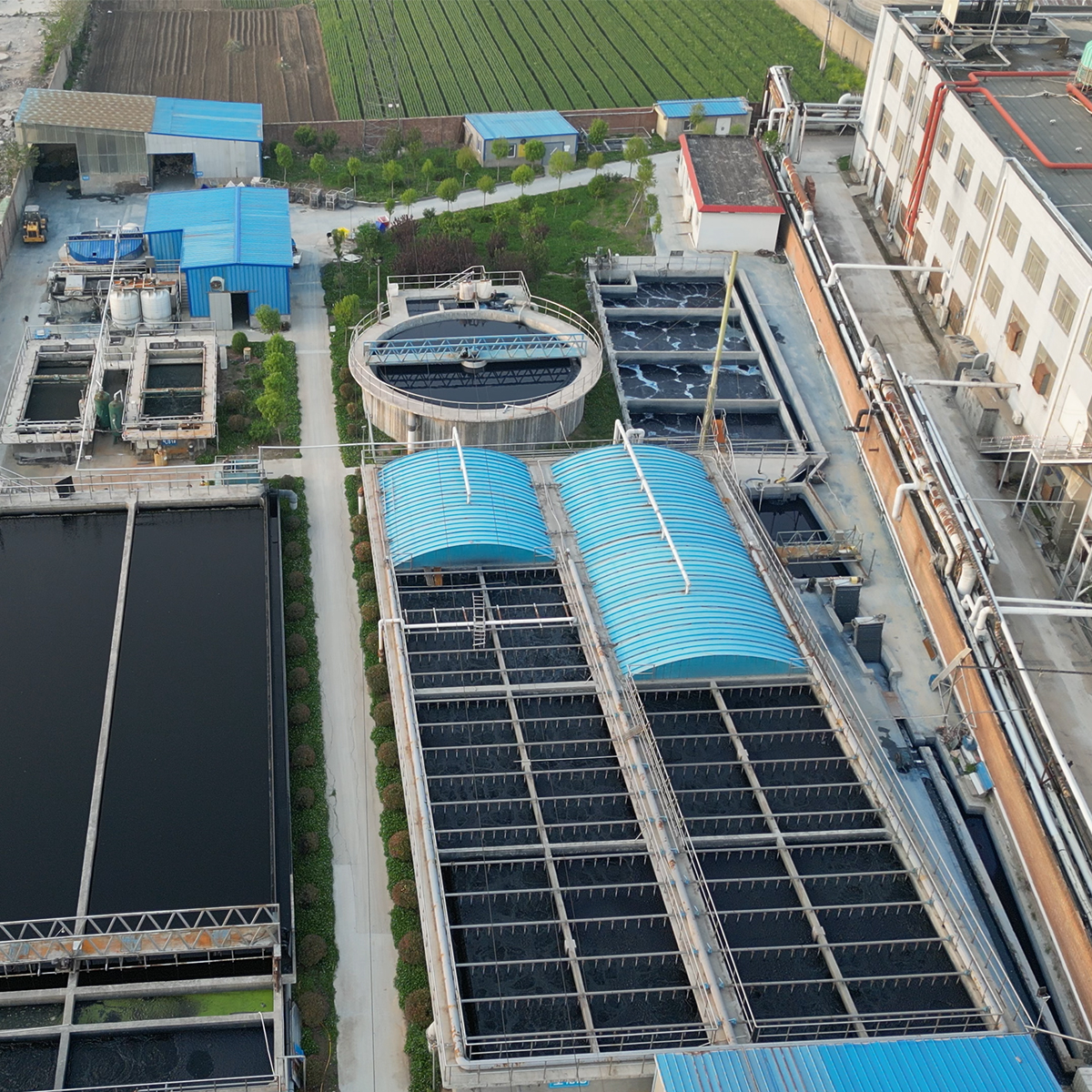
- Sustainable manufacturing practices: Water reuse, energy optimization, and low-waste cutting strategies are embedded into the process.
- Traceability and compliance: Each batch and garment can be traced back through every step, aiding audits, recalls, and brand transparency.
For apparel brands, the impact of these components is profound: faster time to market, tighter cost control, and higher consistency across large volumes. For contract manufacturers, smart jeans capabilities offer differentiated value, enabling them to win and retain customers through reliability and scale. In many regions, including Bangladesh and China, OEM/ODM denim production centers are actively adopting these technologies to fulfill complex global orders while maintaining a lean footprint.
The modern smart jeans factory: a typical workflow
A truly smart jeans facility harmonizes design, engineering, manufacturing, and quality in a loop of continuous improvement. Here is a typical end-to-end flow, with the emphasis on data-driven decision making at each stage:
- Design and development: A brand or design house creates digital patterns, bins colorways, and defines performance targets (stretch, recovery, durability). CAD tools enable rapid prototyping and virtual fit sessions before any physical sample is cut.
- Prototype and fit: Digital twins and 3D visualization help optimize fit and fabric behavior. Physical samples are produced only after successful virtual validation, reducing waste and development time.
- Pre-production planning: BOMs, time studies, and line layouts are simulated in a digital planning environment. This stage determines start times, sequence, and the required mix of processes (e.g., embroidery, hardware, finishing).
- Cutting and material handling: Automated or semi-automated cutting systems maximize fabric yield. Roll-to-roll or panel-based feeding reduces handling and fatigue, while RFID tracking ensures traceability of fabric batches.
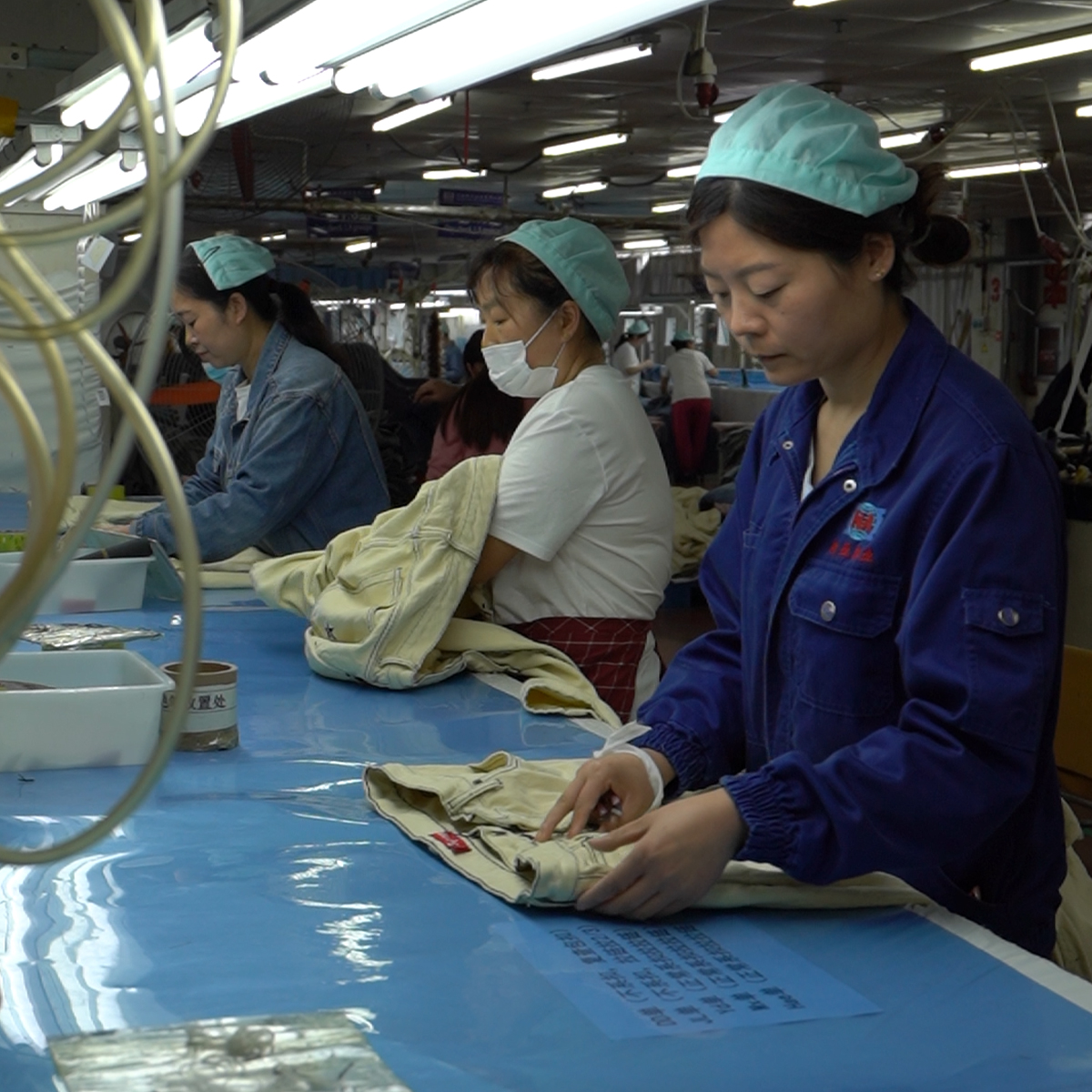
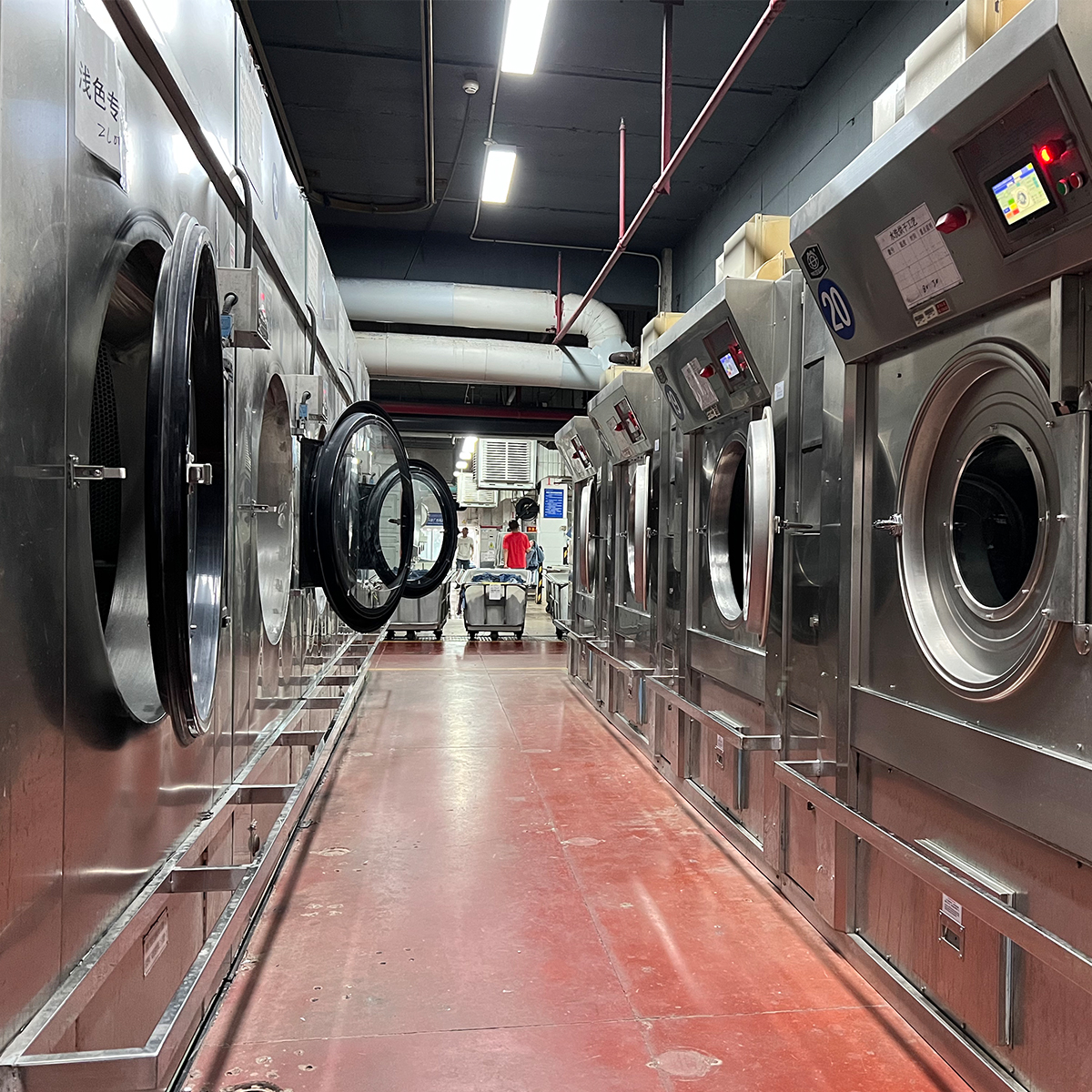
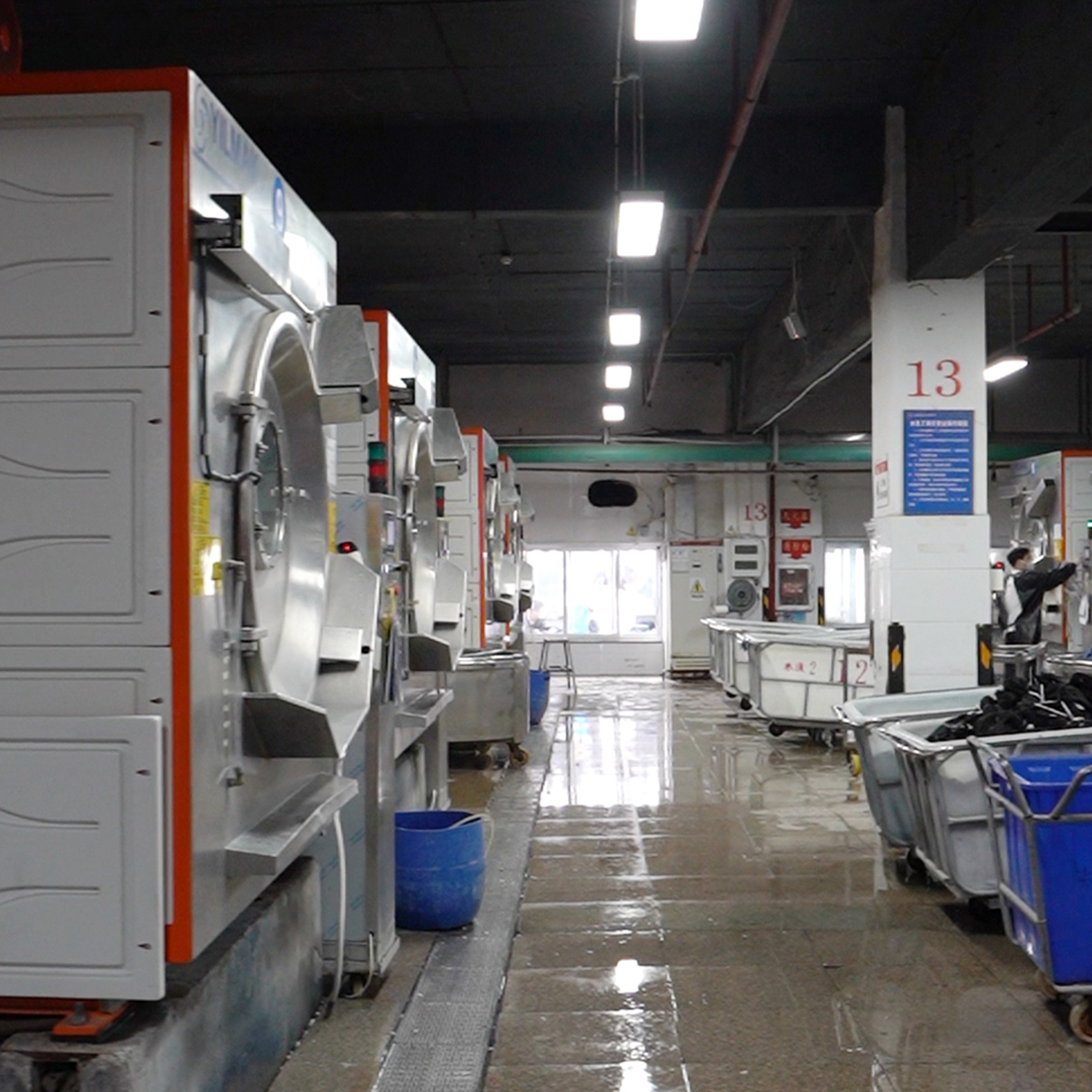
- Sewing and assembly: High-efficiency sewing stations, assisted by robotics or collaborative robots (cobots), maintain consistent seam quality and reduce cycle times on repetitive tasks.
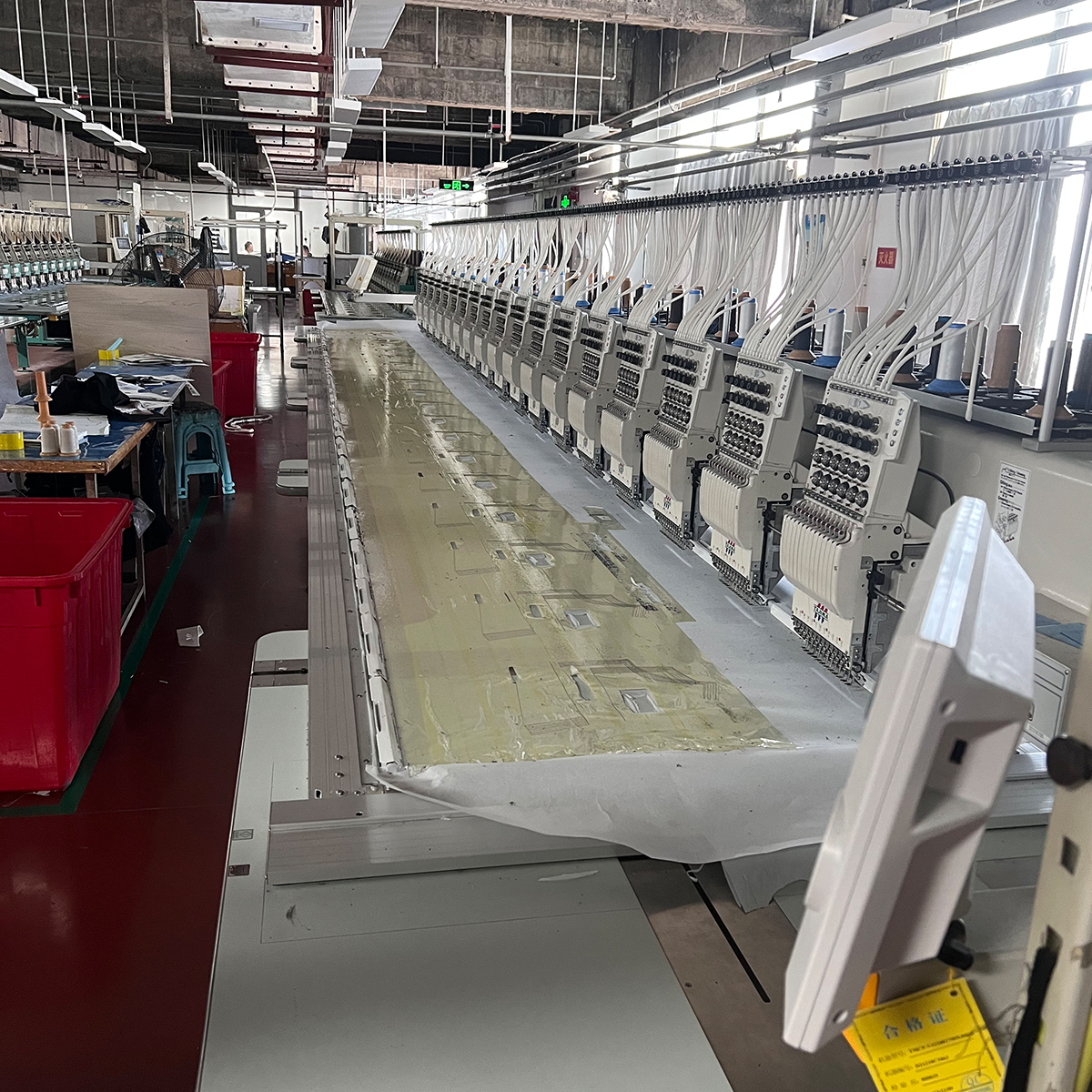
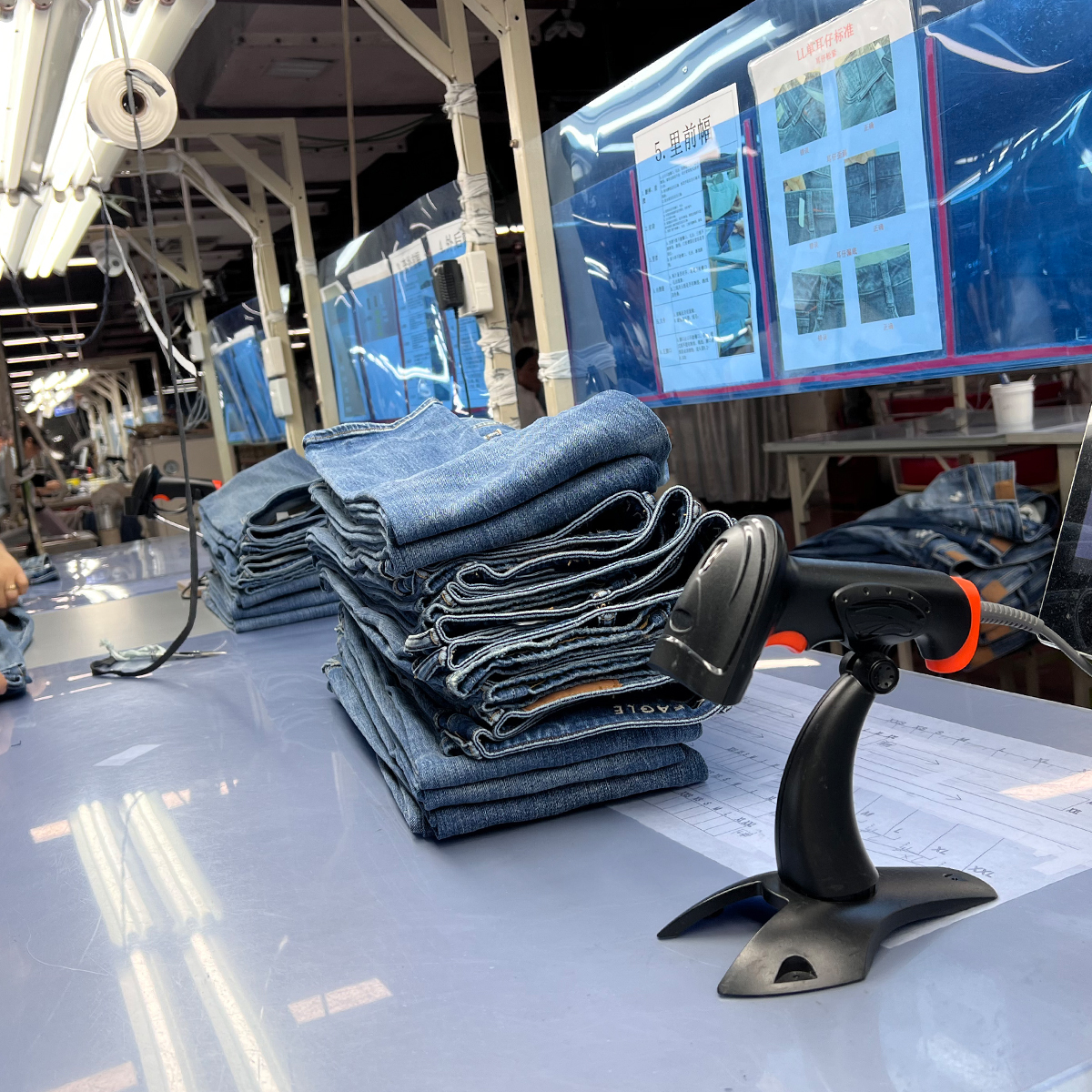
- Finishing and quality controls: Automated pressing, washing, and finishing lines are integrated with inline QC checks. Computer vision detects defects such as misaligned seams, color variations, or fabric inconsistencies in real time.
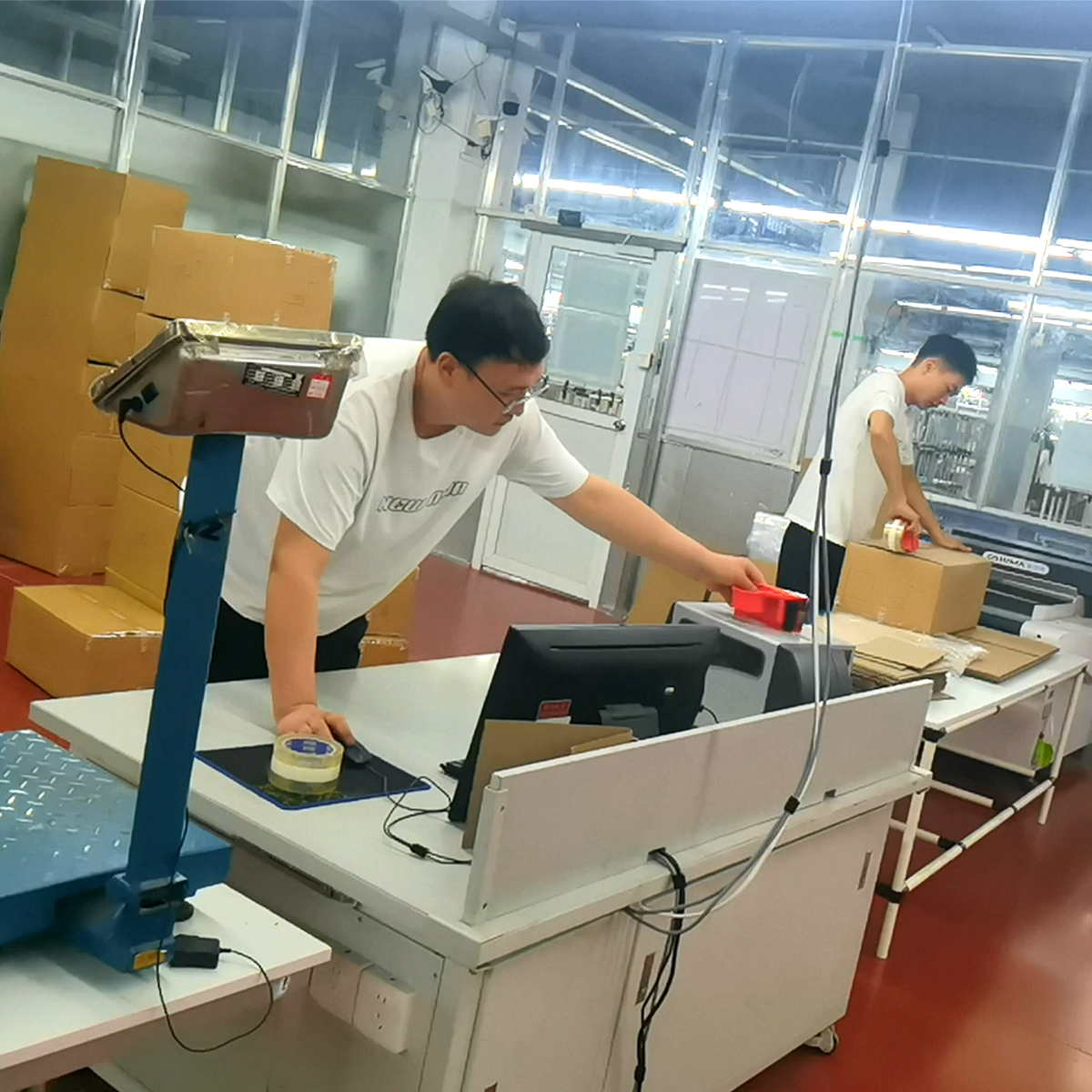
- Packaging and logistics: Finished garments are automatically labeled, bagged, and staged for shipping. Real-time inventory data supports distribution planning and order tracking.
- Post-production analytics: Data from each batch informs continuous improvement—adjusting pattern grading, cutting layouts, or operator assignments to optimize future runs.
In this automated ecosystem, visibility is the key asset. A manager can see cycle times, defect rates, fabric utilization, and energy consumption at a glance, allowing rapid corrective actions before they become costly delays. The result is a smoother, more predictable production rhythm that aligns with the fluctuating demands of global fashion buyers.
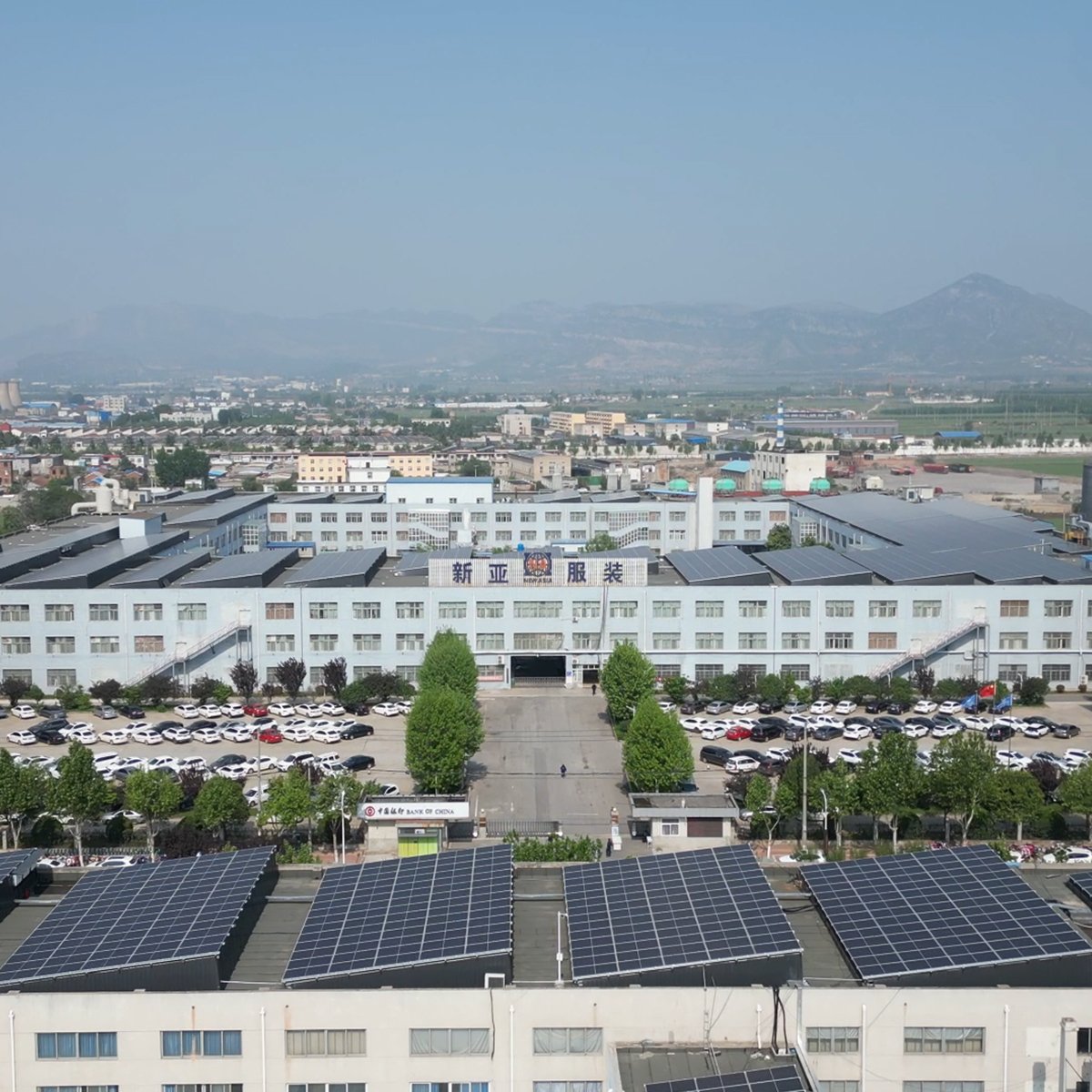
Case study: Smart Jeans Ltd and the Bangladesh denim production landscape
Publicly accessible information highlights Smart Jeans Ltd as a 100% export-oriented garment manufacturer with a focus on denim and related trousers, operating out of Chittagong, Bangladesh. Established in the mid-2000s, the company has built a reputation for serving international brands with reliable capacity for bulk production. While every factory has its unique journey, the Smart Jeans model illustrates several parallel trends in smart manufacturing for denim in emerging markets:
- Export-oriented scale: A focus on larger orders with strict on-time delivery requirements makes efficiency gains from automation especially valuable, reducing throughput times while maintaining quality.
- Specialization in denim and trousers: Denim’s complexity—stretch fabrics, specialized finishes, and hardware—drives the need for flexible, programmable manufacturing equipment and robust quality assurance.
- Capability for collaboration: Partnerships with international buyers demand transparent data exchange and consistent performance across seasonal product lines.
From a buyer’s perspective, working with a smart jeans supplier in a country like Bangladesh offers competitive advantages: lower landed costs due to favorable labor economics, proximity to raw materials and ports, and the ability to scale up production in response to fashion cycles. The smart manufacturing framework amplifies these advantages by delivering predictable lead times, lower defect rates, and better supply chain visibility. For brands evaluating a supplier, the emphasis should be on their readiness to adopt digital tooling, their data governance practices, and their ability to scale automation without sacrificing flexibility.
OEM/ODM partnerships: the broader ecosystem
Beyond individual factories, the denim ecosystem includes comprehensive OEM/ODM manufacturing houses that provide end-to-end denim solutions. A representative partner in this space is Newasia Garment Co., Ltd., a China-based OEM/ODM garment solutions provider with a long-standing track record in denim, casual pants, jackets, and related categories. The company emphasizes large-scale production, agile manufacturing, and robust prototype services, enabling global casualwear brands to bring products to market quickly while maintaining high quality. In a typical smart jeans program, such partners contribute:
- Integrated product development: From concept to pre-production samples, the partner manages the digital thread, ensuring that patterns, fabric spec, and wash plans remain synchronized.
- Fabric and trim optimization: Early collaboration with fabric mills and trim suppliers helps lock in performance targets and reduce post-production changes.
- Scale and flexibility: The ability to ramp production up or down in response to demand helps brands hit seasonal windows without compromising efficiency.
- Quality assurance at scale: Automated QC across lines provides consistent results and traceability for regulatory and brand requirements.
In practice, brands benefit from a seamless flow between the design house, the OEM/ODM partner, and the factory floor. The digital thread—shared digital patterns, production specs, and test results—reduces rework, accelerates approvals, and ensures that every garment meets the brand’s standard before it ships. In a global supply chain, this alignment is critical to meeting both cost constraints and consumer expectations for quality and sustainability.
Benefits of smart jeans manufacturing for brands and factories
The adoption of smart manufacturing principles in denim yields a multi-faceted payoff. Here are the most impactful benefits observed across early adopters and scale-ups:
- Faster time to market: Digital design and automated processes shorten development cycles, enabling brands to respond to trends with greater speed.
- Improved yield and material efficiency: Optimized cutting patterns and intelligent fabric handling reduce waste and lower fabric costs, which are a significant portion of total production expense in denim.
- Lower defect rates and higher consistency: Inline quality checks catch problems earlier, reducing rework and returns while ensuring consistent fit and finish across thousands of units.
- Enhanced traceability and compliance: End-to-end data capture supports social compliance audits, sustainability reporting, and recall readiness.
- Better demand forecasting and supply chain resilience: Real-time visibility from design to delivery reduces silos and enables proactive sourcing and capacity planning.
- Energy and water efficiency: Modern finishing lines often incorporate energy recovery, optimized washing processes, and water reuse, aligning with sustainability targets that many brands prioritize.
Implementation pathways: from pilot to full-scale smart jeans production
For brands and factories beginning their smart manufacturing journey, a pragmatic, staged approach is essential. Below is a practical blueprint to guide investment and rollout:
- Assess readiness: Map current processes, data maturity, and organizational readiness. Identify bottlenecks where digital tools can create the largest impact (e.g., pattern development, cutting efficiency, or QC).
- Define objectives and ROI: Set specific targets for throughput, defect reduction, energy use, and lead time. Build a business case that accounts for initial capital, training, and ongoing maintenance.
- pilot with a module: Start with a high-leverage area such as digital patterning and automated cutting or inline QC. Use a small, controllable test line to measure impact before scaling.
- Invest in flexible automation: Choose modular automation platforms that can adapt to new SKUs and different finishes. Avoid locking into rigid systems that hinder future product changes.
- Integrate data systems: Implement an integrated data backbone (ERP, MES, PLM) that consolidates design, planning, and production data. Establish standards for data quality, access control, and cybersecurity.
- Upskill the workforce: Train operators, technicians, and managers on digital tools, troubleshooting, and continuous improvement methodologies. A culture of data-driven decision making is essential.
- Scale with governance: As lines expand, implement standardized work, process control limits, and KPIs. Use dashboards to maintain visibility across plants and partner factories.
- Foster supplier collaboration: Engage mills, wash plants, and trimming suppliers in the digital thread so changes propagate smoothly across the supply chain.
Successful adoption hinges on balancing automation with flexibility. Denim programs often demand frequent changes in washes, finishes, and trims triggered by fashion cycles. The most effective smart factories are those that maintain adaptability while benefiting from standardization and repeatable best practices.
Designing for the future: trends shaping smart jeans manufacturing
The next era of denim production is defined by three broad themes: deeper data integration, smarter materials, and circularity. Brands and manufacturers should watch these trends as they plan capital investments and supplier partnerships.
- Digital twins and AI-driven design: Virtual prototypes and algorithmic optimization help predict fabric behavior, fit, and performance before a single piece is cut, dramatically reducing sampling rounds.
- Robotics and cobotics on the line: Collaborative robots assist human operators in repetitive, precision-based tasks, freeing skilled workers to focus on more complex operations and quality decisions.
- Smart textiles and performance fabrics: As denim finishes and coatings become more sophisticated, production lines need to handle new materials with different shrinkage, drape, and color properties.
- Cloud-based PLM and supplier networks: A connected ecosystem across design houses, mills, and manufacturers enables faster, more coordinated product development and launches.
- Sustainability as a built-in feature: Waterless washes, closed-loop dyeing, and energy recovery become standard design constraints, influencing both process choice and long-term cost models.
A quick guide for selecting a smart jeans manufacturing partner
Choosing the right partner is crucial for a successful smart jeans program. Here are practical criteria brands can use when evaluating potential factories or OEM/ODM partners:
- Technology maturity: Does the facility already operate with digital patterning, automated cutting, inline QC, and integrated data systems? Are there documented case studies or performance metrics?
- Scalability: Can the line ramp up to large volumes while preserving quality? Is the automation modular and adaptable to new SKUs?
- Data governance and security: How is data protected? Are there clear data-sharing agreements and cyber risk mitigations in place?
- Sustainability commitments: What are the factory’s targets for water, energy, waste, and chemical management? How are they tracked and reported?
- People and culture: Is there a program for skills development, continuous improvement, and cross-functional collaboration with design teams?
- Supply chain integration: How well can the partner connect with mills, laundries, and logistics providers to support a seamless digital thread?
- References and track record: Can the partner demonstrate consistent on-time delivery, quality outcomes, and the ability to support multiple brands concurrently?
For brands seeking to accelerate their smart jeans journey, a partner like the Bangladesh-based Smart Jeans factory network can offer a proven export orientation and denim focus, while OEM/ODM partners in Asia—such as Newasia Garment Co., Ltd.—provide layer-cake capabilities across design, development, and large-scale production. The optimal choice is a partner whose strategic priorities align with yours: speed to market, quality consistency, and a credible path to sustainable, data-driven manufacturing.
The bottom line: embracing the denim revolution
The garment industry is witnessing a quiet revolution: factories that embrace digital tooling, automation, and data-driven operations are not just more efficient, they are more agile. They can absorb demand shocks, test new concepts quickly, and maintain consistent quality across tens of thousands of units. For brands and factories alike, smart jeans manufacturing is not a speculative trend but a practical framework for competing in a global market that values speed, transparency, and responsible production. As markets evolve, the synergy between design teams, fabric suppliers, and factory floors will increasingly rely on a shared digital thread—one that keeps everyone aligned from first sketch to final shipment, and every pair of jeans in between.
In this evolving landscape, the denim story remains grounded in craft and character. Smart manufacturing amplifies those traits by removing guesswork, reducing waste, and delivering repeatable quality at scale. The best outcomes arise when brands choose partners who bring not only machines and software but a collaborative mindset: a willingness to adapt, iterate, and learn together. When that happens, the promise of smart jeans becomes a tangible reality—the future of denim is here, stitched with data, wired through automation, and worn by customers who demand more from their favorite pair of jeans.