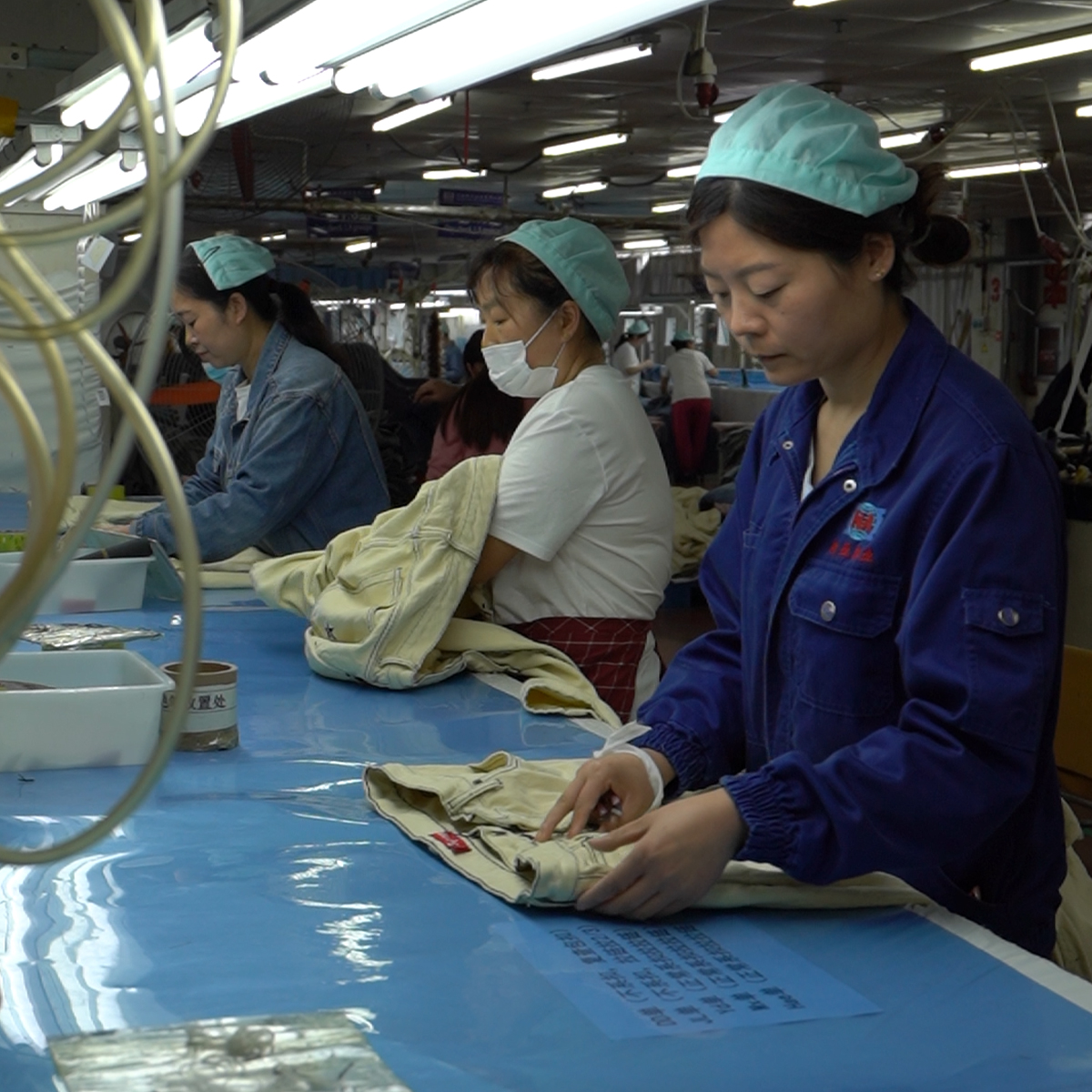
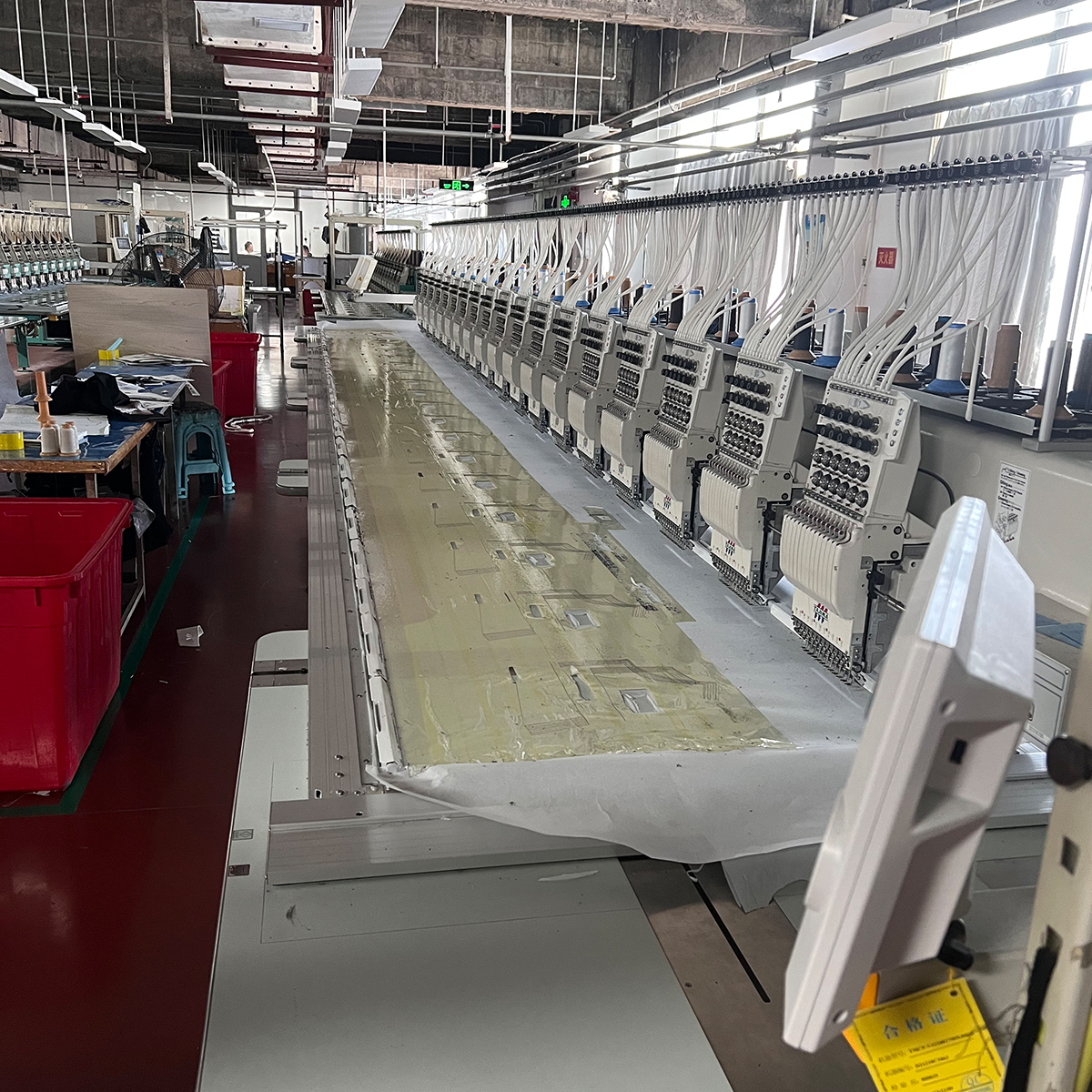
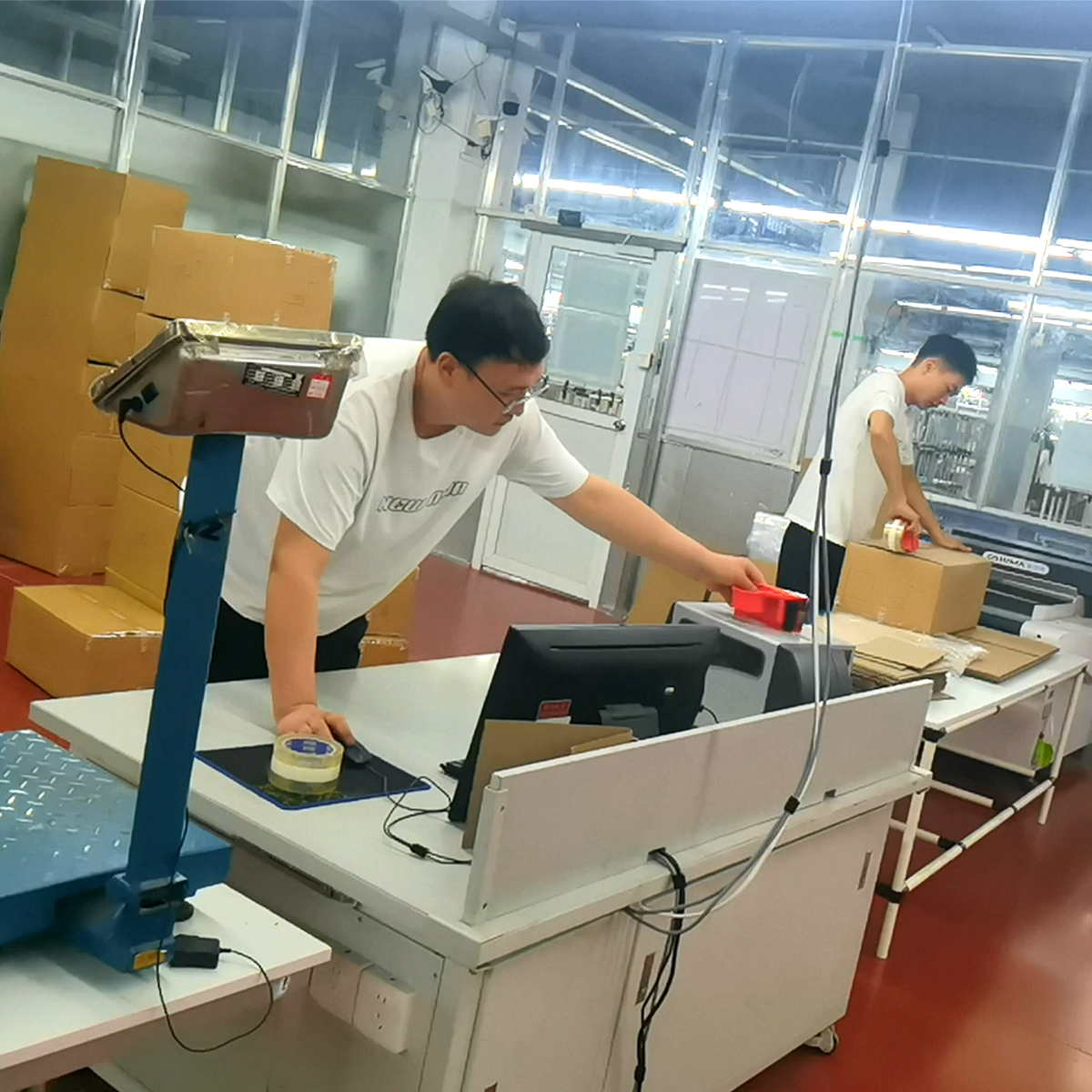
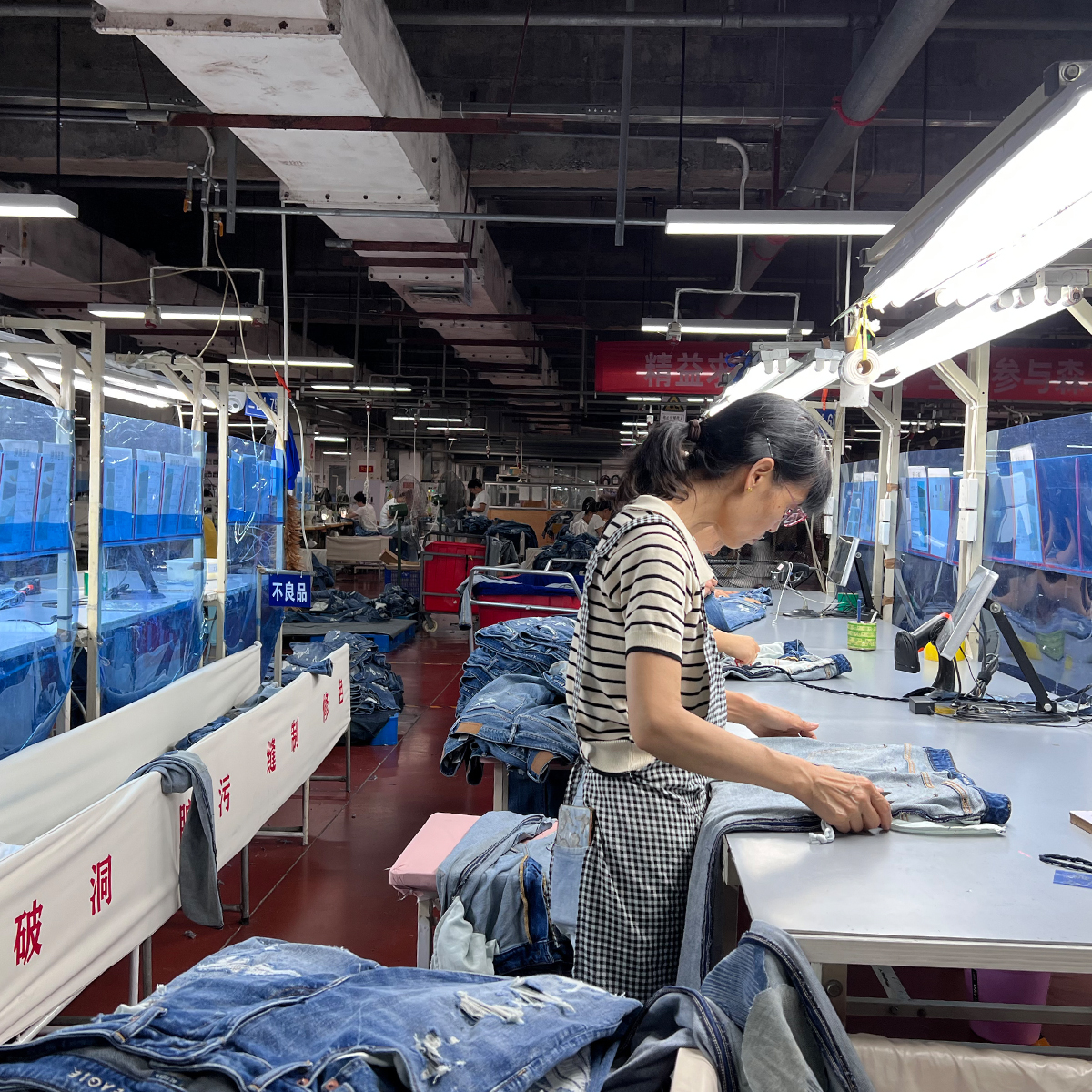
Jeans have become a staple in wardrobes around the world, transcending trends and cultures. From classic blue denim to trendy cuts and styles, jeans are more than just a piece of clothing—they’re a universal symbol of comfort and self-expression. But have you ever wondered where these beloved garments originate? In this blog post, we’ll take a deeper look into the manufacturing of jeans, exploring the key regions responsible for their production, the processes involved, and how globalization plays a significant role in the denim industry.
The History of Jeans Manufacturing
The journey of jeans began in the 19th century when Levi Strauss, a Bavarian immigrant, and tailor Jacob Davis created durable work trousers for gold miners. The original jeans were made from a heavy cotton fabric known as denim, which was woven in Nîmes, France. The term ‘denim’ comes from the French phrase “serge de Nîmes,” meaning “serge from Nîmes.” Over the years, jeans have evolved from utilitarian workwear to high-fashion statements, leading to a massive global manufacturing industry.
The Major Producers of Jeans
Today, jeans are manufactured in various countries, with several key regions standing out for their production capabilities. These include:
- China: As one of the largest producers of garments in the world, China dominates the jeans manufacturing scene. With advanced technology and a vast labor force, Chinese factories are equipped to produce millions of pairs of jeans each year. Popular brands often outsource their production to China to benefit from lower costs.
- Bangladesh: Over the last two decades, Bangladesh has emerged as a significant player in the denim industry. With renowned manufacturers and a favorable cost of production, the country is known for producing high-quality jeans for brands around the globe. The booming garment sector has transformed the nation’s economy, although it has sparked discussions about labor conditions and sustainability.
- Vietnam: Vietnam is gaining traction as an emerging hub for jeans manufacturing. With competitive labor costs and a focus on improving working conditions, Vietnamese factories are attracting brands looking to diversify their supply chains while maintaining quality standards.
- India: India has a long-standing tradition of cotton production, which complements its growing denim industry. Regional manufacturers are increasingly adopting sustainable practices, such as water-efficient dyeing techniques, to meet the rising demand for eco-friendly products.
- Turkey: Turkey is known for its high-quality denim production. It serves as a strategic manufacturing location for brands looking to supply the European market quickly. The Turkish denim industry is notable for its innovative textile development and focus on sustainability.
The Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of jeans involves several steps, each of which contributes to producing the final product. Here’s a breakdown of the typical stages:
1. Sourcing Raw Materials
The journey begins with sourcing raw materials. Cotton is the primary ingredient used in jeans production. The cotton is spun into yarn, which is then woven into denim fabric. The quality of the cotton and the weaving technique significantly affect the final product’s texture and durability.
2. Dyeing and Finishing
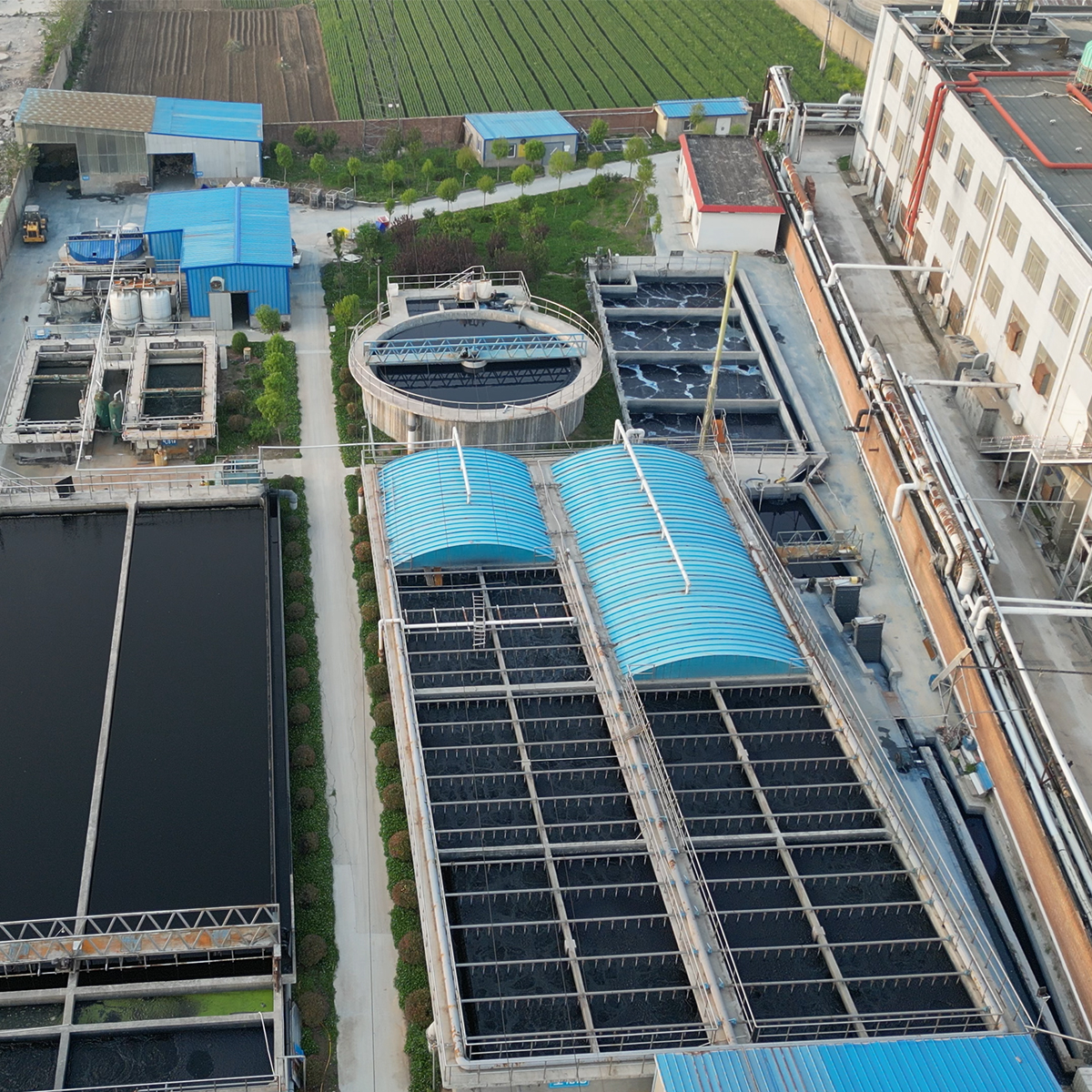
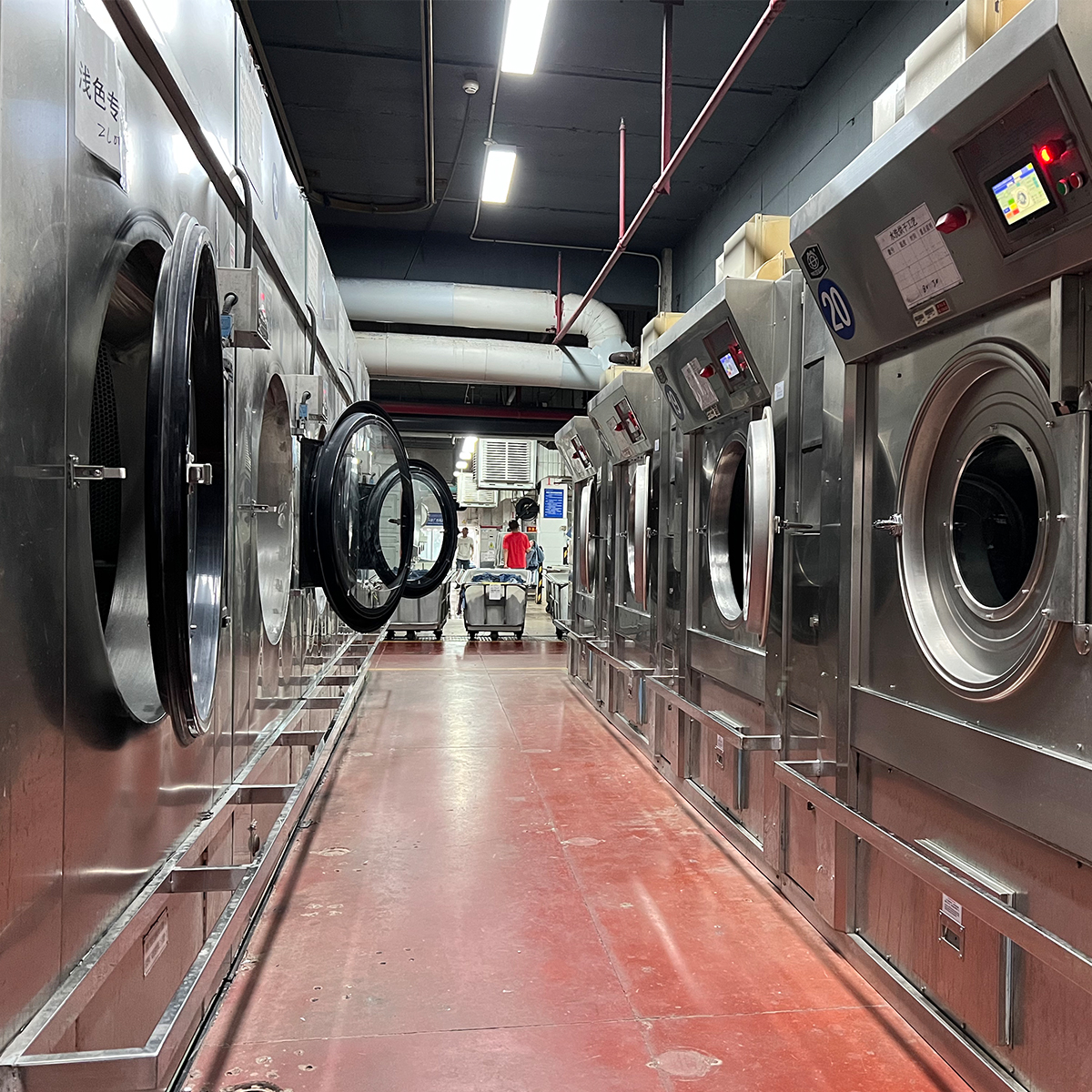
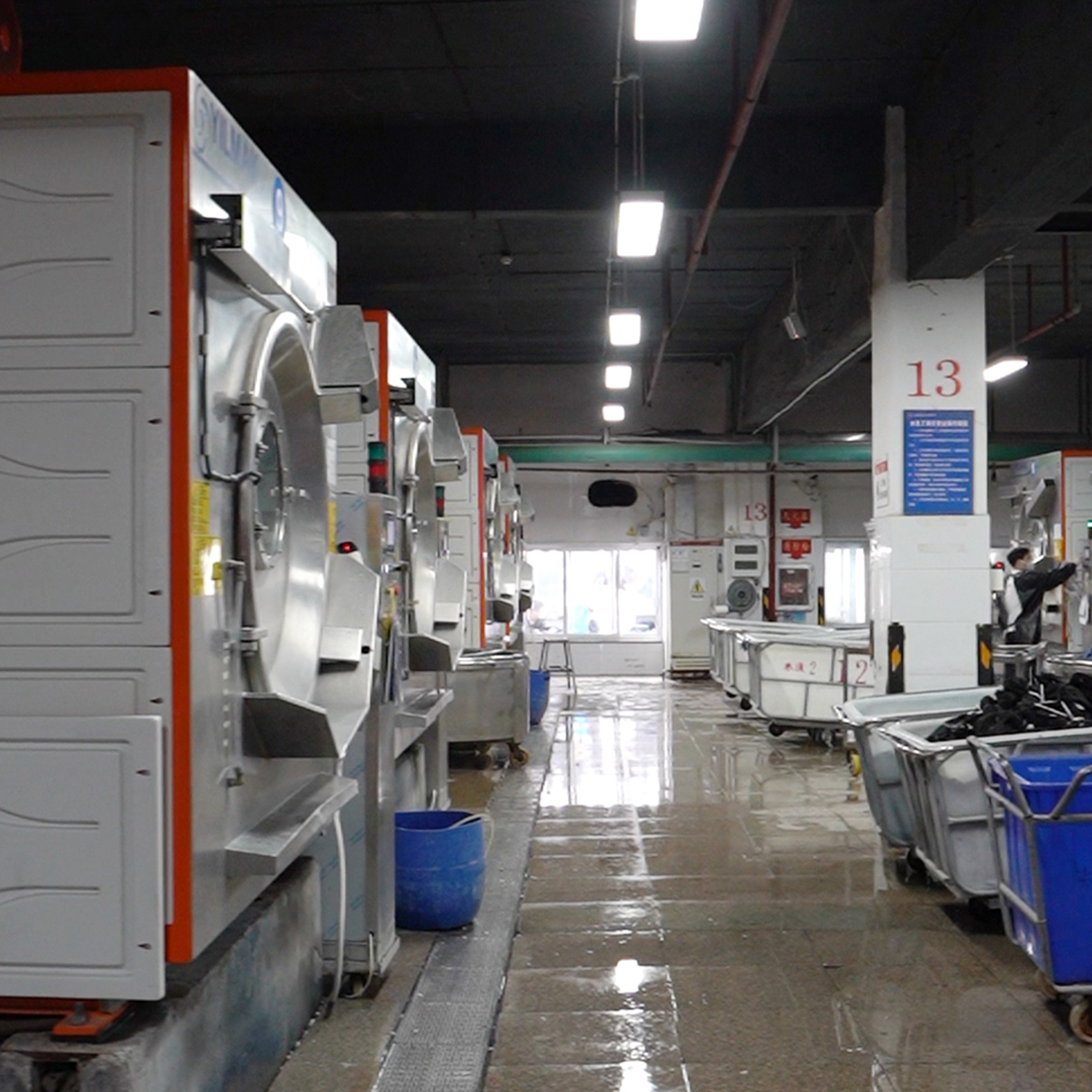
The denim is usually dyed with indigo, giving jeans their characteristic blue hue. Dyeing can be done through various methods, including rope dyeing and ring dyeing. After dyeing, the fabric undergoes finishing processes, such as washing and softening, to enhance its comfort and appearance.
3. Cutting and Sewing
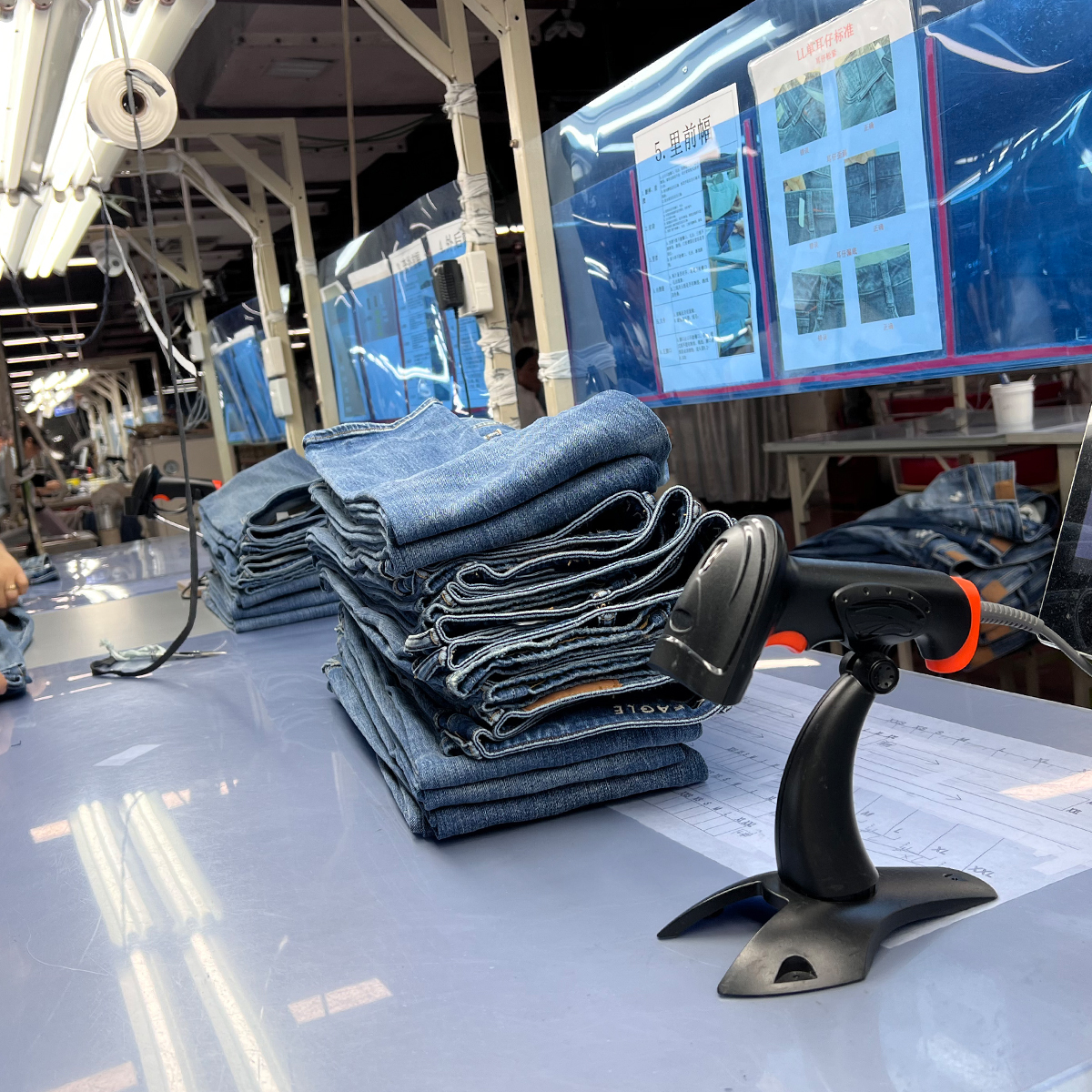
Once the fabric is ready, it is cut into different patterns based on the desired style of the jeans. This stage requires precision to ensure the pieces fit together seamlessly. After cutting, the fabric pieces are sewn together, creating the basic structure of the jeans.
4. Quality Control
Quality control is a crucial step in denim manufacturing. Before the jeans are packaged and shipped, they are inspected for defects, ensuring that only high-quality products reach the market.
Globalization and the Denim Industry
The denim industry is a prime example of globalization in action. With brands sourcing materials and labor from different parts of the world, the production of jeans involves a complex network of supply chains. This interconnectedness allows brands to take advantage of cost efficiencies and specialized manufacturing capabilities.
However, this globalization has also raised concerns about ethical practices and sustainability. With increased scrutiny on labor conditions and environmental impact, many manufacturers are working towards adopting more responsible practices. Brands are now focusing on ethical sourcing, fair labor practices, and environmental sustainability, reflecting a growing demand from consumers for transparency and accountability.
The Future of Jeans Manufacturing
As we look to the future, the jeans manufacturing industry is likely to undergo significant transformations. Innovations in technology, such as automated production processes and 3D printing, may revolutionize how jeans are made. Additionally, the rise of sustainable and eco-friendly practices will play a crucial role in shaping the industry’s future.
Moreover, as consumers become increasingly aware of the impact their clothing choices have on the environment, brands may prioritize sustainable practices in their manufacturing processes. This shift could lead to more local production to reduce the carbon footprint associated with transportation, further changing the landscape of jeans manufacturing.
Conclusion
The journey of jeans from manufacturer to consumer is complex and deeply intertwined with global trade, culture, and technology. Understanding where jeans are manufactured and the processes involved opens a window into the rich tapestry of the fashion industry. As we continue to wear, love, and celebrate jeans, awareness of their origins and the ethics behind their production will help shape a more sustainable and conscious future for fashion.